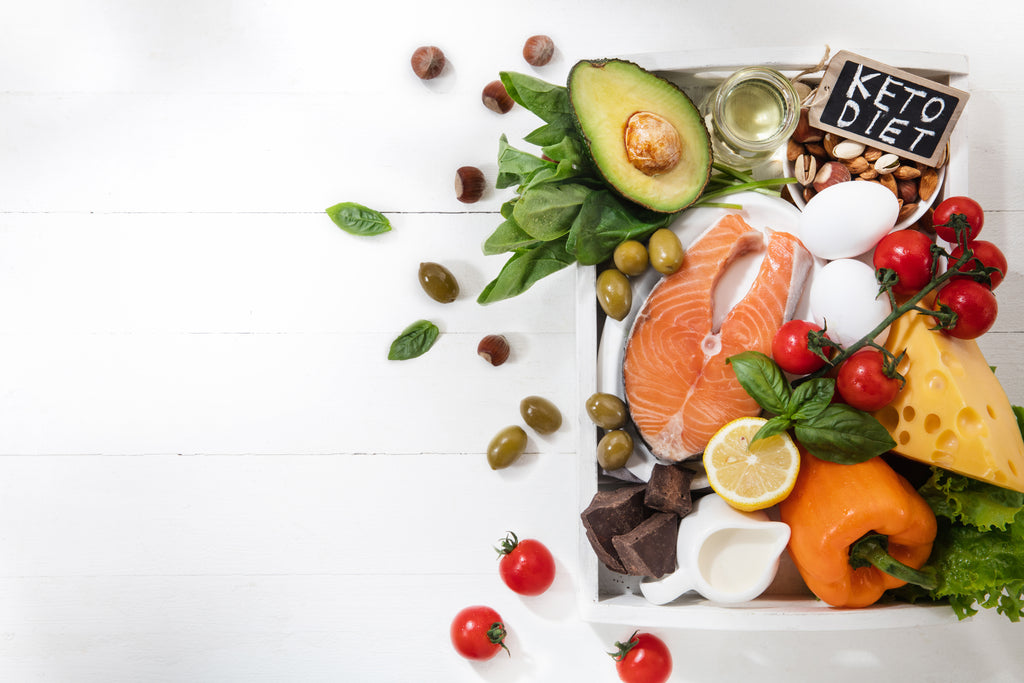
Ketogenic Diets - A Complete Overview
Posted by Just Fitter on
The ketogenic diet is a very low-carb and high-fat diet that shares similarities with the Atkins and low-carb diet. When you reduce carbs significantly it puts your body in a metabolic state called ketosis, hence, the name Keto Diet. While your body is in ketosis it uses fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates but this is a delicate balance to adjust to and maintain. Fortunately, there are different ways to measure it, blood, urine, and breath tests which can tell you if your body is in ketosis or are easy to find on online markets. In general, it takes 2-4 days to reach ketosis. However, some people find it takes a week or longer to reach this state. You have to make sure that your body is in ketosis while on this diet. Otherwise, you are just eating a high-fat diet and that's not good for anyone. That being said there may be some benefits to it. A ketogenic diet can cause a significant reduction in blood sugar and insulin level. It has also been shown that this is effective for weight loss, type 2 diabetes, and managing childhood epilepsy the diet is filling and it slashes your hunger hormones. Many people like it that they are able to lose weight on it without counting calories or tracking food intake. There are multiple types of keto diets out there but the standard ketogenic diet is the best researched.
Different Types of Ketogenic Diet
-
Standard Ketogenic Diet - this is a low carb, moderate protein, and high-fat diet. It typically contains 70-75 percent fat, 20 percent protein, and about 5-10 percent carbohydrates.
In terms of grams per day, a typical standard ketogenic diet would be:- 20-50 g of carbohydrate
- 40-60g of protein
- No set limit on the fat
Ketogenic diets include non-starchy vegetables as these are very low in carbohydrates. This kind of diet has significantly helped in weight loss, blood glucose control, and heart health improvement. - Very-Low-Carb Ketogenic Diet - this is usually referred to as a standard ketogenic diet since both require very low carbohydrate intake.
- Well Formulated Ketogenic Diet (WFKD) - The WFKD follows a similar blueprint as a standard ketogenic diet. Well formulated means that the macronutrients of fat, protein, and carbohydrate meet the ratios of the standard ketogenic diet and therefore provide the best chance of ketosis occurring.
-
MCT Ketogenic Diet - it follows the outline of a standard ketogenic diet but has a focus on medium-chain triglycerides or MCT to provide much of the fat content in your diet. MCTs are commonly found in coconut oil. This diet is used to treat epilepsy because the theory is that MCTs allows people to consume more carbohydrate and protein while keeping in ketosis. This is because MCTs provide more ketones per gram of fat than the long-chain triglycerides that are present in normal dietary fat.
Important Note: MCT can lead to stomach upset and diarrhea if consumed largely on its own. To prevent this, it’s best to have meals with a balance of MCTs and non - MCT fat. - Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet - this is a standard ketogenic diet with calorie restriction. However, studies show that with or without calorie restrictions it still tends to be successful due to satiating effect of eating fat, and being in ketosis tends to help prevent over-eating in itself.
- Cyclical Ketogenic Diet - also known as carb backloading in which you eat very low carbohydrates on ketogenic diet days and 2 days with a higher intake of carbohydrates this diet is intended for athletes who can use the higher carbohydrate dates to replenish the glycogen lost from muscles during workouts.
- Targeted Ketogenic Diet - is a compromise between a standard ketogenic diet and a cyclical ketogenic diet that allows you to consume carbohydrates on your workout times.
- High Protein Ketogenic Diet - this diet is most effective for weight loss, this requires a ratio of 35 percent protein, 60 percent fat, and 5 percent carbohydrate.
What is Ketosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which your blood has a high concentration of ketones, namely beta-Hydroxybutyrate. It occurs when your body starts using fat as its main fuel source due to limited access to glucose, or blood sugar, typically caused by starvation, fasting, or following a very low carb diet.
Different ways to test ketones:
- Blood - you will need to use a blood ketone meter; you get a reading of the amount of β-hydroxybutyrate circulating in your blood. It requires a finger-stick to produce a very small drop of blood for testing.
- Breath - once the device is set up, a deep exhale — from the bottom of your lungs into the device — is all that it takes to get a measurement.
- Urine - The low-tech way to test for ketosis is with urine test strips designed to check for the ketone acetoacetate. Most of the strips are available online and it comes with instructions that are most convenient for testing ketones.
Benefits:
- Epilepsy - for patients who were unresponsive to the epilepsy treatment, ketogenic has been introduced in the 1920s, especially to children.
- Weight loss - when you are in a state of ketosis your body uses fat-derived ketones produced in the liver to fuel itself which significantly leads to weight loss.
- Type 2 diabetes - research has shown that following a ketogenic diet is an effective strategy for managing blood sugar levels in those with type 2 diabetes.
Downsides and Risks:
If you’re intentionally following a ketogenic diet, you may wonder whether you’ve achieved ketosis. Here are some common signs and symptoms:
- Bad breath, which is caused by a ketone called acetone
- Weight loss
- Reduced appetite
- Headache
- Nausea
- Brain fog
- Fatigue
- Keto flu - symptoms which can feel similar to the flu, are caused by the body adapting to a new diet consisting of very little carbohydrates.
Foods to reduce to achieve the state of ketosis:
- Grains
- Legumes
- Potatoes
- Fruit
- Candy
- Soda and Sugar-sweetened beverages
- Condiments and sauce that contains sugar, like ketchup and barbecue sauce
To put this into perspective, 1 slice (32 grams) of bread contains roughly 15 grams of carbohydrates, while 1 cup (186 grams) of cooked rice contains around 53 grams of carbohydrates. People may choose to follow a keto diet to lose weight, better manage their blood sugar levels, or reduce the incidence of epilepsy-related seizures, among other reasons.
Conclusion:
The ketogenic diet is a very low-carb and high-fat diet that shares similarities with the Atkins and low-carb diet. Though this diet has a lot of benefits in easing out health issues like type 2 diabetes there are risks and side effects that we need to consider. We still need to consider doctors’ advice and do research to make it effective and safe.
Reference: